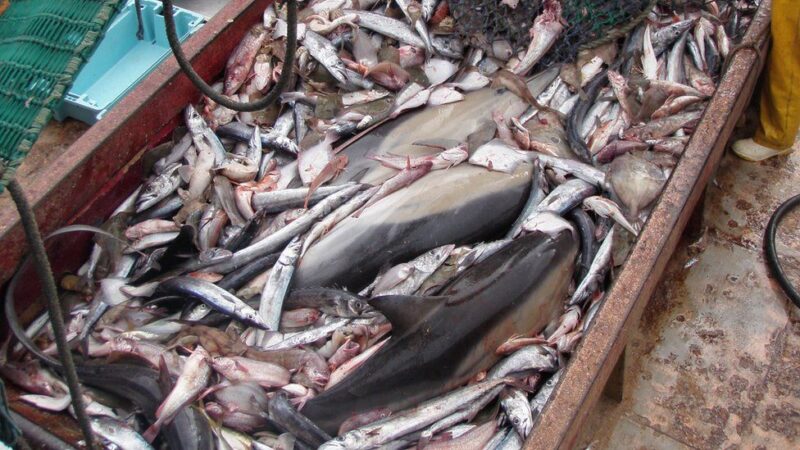
Bycatch is a term used in the fishing industry to describe the incidental capture of non-target species during fishing operations. It’s a problem that often goes unnoticed, but its impacts are far-reaching and devastating to marine life, ecosystems, and economies.
Understanding the Impact of Bycatch
Before diving into the specifics, it’s important to understand the sheer scale of bycatch. It’s estimated that globally, bycatch accounts for a staggering 40% of the world’s total catch. This means that nearly half of all marine life caught is unintentionally caught and often discarded back into the sea, dead or dying.
The Environmental Consequences of Bycatch
Destruction of Marine Ecosystems
Bycatch doesn’t just impact the species that are unintentionally caught; it has a cascading effect on the entire marine ecosystem. For instance, the removal of certain species can create imbalances in the food chain, leading to overpopulation of some species and endangerment of others.
Endangerment of Marine Species
Many of the species affected by bycatch are already vulnerable or endangered. The additional pressure from bycatch can push these species closer to extinction, reducing biodiversity in our oceans.
Disruption of the Food Chain
The removal of certain species from the food chain can also have a ripple effect, impacting other species that rely on them for food. This can lead to a decline in the populations of predator species, further destabilizing the marine ecosystem.
The Economic Cost of Bycatch
Waste of Resources
The economic implications of bycatch are also significant. When non-target species are caught and discarded, the resources used to catch them, including fuel, labor, and gear, are wasted. This represents a significant financial loss for the fishing industry.
Financial Impact on Fishing Industries
The financial burden of bycatch is often shouldered by fishing communities, particularly in developing countries where fishing is a major source of income and food. The loss of income due to bycatch can have a profound impact on these communities.
Implications for Local Communities
In some cases, bycatch can also lead to conflicts between different fishing communities, as they compete for dwindling resources. This can exacerbate existing tensions and lead to social and political unrest.
Mitigating Bycatch: Current Efforts
Implementing Sustainable Fishing Practices
Efforts are being made to mitigate the impact of bycatch. One of the primary strategies is to implement sustainable fishing practices that minimize the capture of non-target species. This includes using selective gear, such as circle hooks and turtle excluder devices, which can help reduce bycatch.
Advancements in Fishing Technology
Technological advancements are also playing a role in reducing bycatch. Innovations such as acoustic pingers, which deter marine mammals from approaching fishing gear, and LED lights, which can reduce the capture of non-target species, are proving effective.
Educating Fishermen and Consumers
Education is another crucial component of bycatch mitigation. By educating fishermen about sustainable practices and consumers about the impact of their choices, we can create a more sustainable and responsible fishing industry.
The Role of Consumers in Combating Bycatch
Making Informed Choices
Consumers have a significant role to play in combating bycatch. By making informed choices about the seafood they consume, they can support sustainable fisheries and reduce the demand for overfished species.
Supporting Sustainable Seafood Brands
There are a number of organizations and certifications, such as the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC), that aim to promote sustainable fishing practices. By choosing seafood that is certified by these organizations, consumers can help drive the industry towards more responsible practices.
Conclusion and Future Prospects
In conclusion, bycatch is a complex issue that requires a multi-faceted approach. While significant progress has been made in mitigating its impact, there is still much work to be done. The future of our oceans depends on our ability to strike a balance between meeting our needs and protecting the delicate marine ecosystems that sustain us.
Similar Articles
- Black Carbon: Its Sources, Properties, and Impact on Human Health and the Environment
- Bioregions: Exploring the Significance and Benefits of Bioregionalism
- Biomass Energy: A Sustainable Solution for a Greener Future
FAQs
What is bycatch and why is it a problem?
Answer: Bycatch refers to the unintentional capture of non-target species during fishing operations. It’s a problem because it results in the waste of resources and the unnecessary harm or death of marine life. This can have cascading effects on marine ecosystems and economies.
How does bycatch affect marine ecosystems?
Answer: Bycatch can significantly impact marine ecosystems. The removal of non-target species can create imbalances in the food chain, leading to overpopulation of some species and endangerment of others. This can cause a decline in biodiversity and further destabilize marine ecosystems.
What are some strategies for reducing bycatch?
Answer: There are several strategies for reducing bycatch, including implementing sustainable fishing practices, using selective gear, and adopting technological advancements. Education of both fishermen and consumers about the impact of bycatch and sustainable practices is also crucial in combating this issue.
How can consumers help combat bycatch?
Answer: Consumers can help combat bycatch by making informed choices about the seafood they consume. Supporting sustainable fisheries, choosing seafood certified by organizations promoting sustainable practices, and spreading awareness about bycatch can all contribute to reducing its impact.
What role do certifications like the Marine Stewardship Council play in promoting sustainable fishing practices?
Answer: Certifications like the Marine Stewardship Council (MSC) play a significant role in promoting sustainable fishing practices. They provide a framework for fisheries to follow sustainable practices and offer a label that consumers can trust. This helps drive the industry towards more responsible practices and reduces the demand for overfished species.