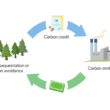
Carbon dioxide, or CO2, is a colorless, odorless gas that is naturally present in Earth’s atmosphere in trace amounts. It is a vital component of the carbon cycle, a series of processes through which carbon atoms move through the environment.
The Carbon Cycle
The carbon cycle starts with the absorption of carbon dioxide by plants through a process called photosynthesis. This carbon is then transformed into glucose, which is used by plants for energy. When animals eat plants, they also consume the carbon, which becomes part of their bodies. Through respiration and decomposition, this carbon is eventually released back into the atmosphere, completing the cycle.
Sources of Carbon Dioxide
Natural Sources
Carbon dioxide is naturally emitted through volcanic eruptions, forest fires, and the respiration of living organisms. These natural sources have been present for millions of years and have contributed to the balance of carbon in the atmosphere.
Human-Induced Sources
Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels such as coal, oil, and natural gas, have significantly increased the levels of co2 in the atmosphere. Deforestation and land-use changes also contribute to higher CO2 emissions, as fewer trees are available to absorb the gas.
Effects of CO2 on the Environment
Greenhouse Gas and Global Warming
Carbon dioxide is a major greenhouse gas, which means it traps heat from the sun in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming. The increase in atmospheric CO2 levels due to human activities has been a significant factor in the rise of global temperatures.
Ocean Acidification
When CO2 is absorbed by seawater, it reacts with the water to form carbonic acid. This process, known as ocean acidification, can harm marine ecosystems, particularly coral reefs and shell-forming organisms.
Carbon Dioxide in the Human Body
Role in Respiration
CO2 plays a crucial role in human respiration. It is a waste product of the metabolism of food, and it is transported by the blood to the lungs, where it is expelled from the body when we exhale.
Health Risks
While carbon dioxide is not toxic in low concentrations, high levels of CO2 can be harmful to human health. Exposure to elevated levels can cause headaches, dizziness, and in extreme cases, unconsciousness or death.
Mitigating Carbon Dioxide Emissions
Carbon Capture and Storage
Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a technology that captures carbon dioxide emissions from industrial processes and power plants and stores them underground. This prevents the CO2 from entering the atmosphere and contributing to global warming.
Renewable Energy Sources
Transitioning to renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, can significantly reduce CO2 emissions. These sources produce electricity without emitting CO2, making them an essential part of any strategy to mitigate climate change.
Conclusion
CO2 is a vital component of the carbon cycle, but human-induced emissions have led to an increase in atmospheric CO2 levels, contributing to global warming and ocean acidification. To address these challenges, we need to reduce our reliance on fossil fuels, protect and restore forests, and invest in carbon capture and storage technologies. By doing so, we can safeguard our planet for future generations.
Similar Articles
FAQs
What is carbon dioxide?
Carbon dioxide (CO2) is a colorless, odorless gas that is naturally present in Earth’s atmosphere in trace amounts.
How does carbon dioxide contribute to global warming?
Carbon dioxide is a major greenhouse gas, which means it traps heat from the sun in the Earth’s atmosphere, leading to global warming.
What are some sources of carbon dioxide emissions?
CO2 is emitted from natural sources such as volcanic eruptions and forest fires, as well as human-induced sources like the burning of fossil fuels and deforestation.
What is ocean acidification and how is it related to Co2?
Ocean acidification is the process by which co2 is absorbed by seawater and reacts with the water to form carbonic acid. This can harm marine ecosystems, particularly coral reefs and shell-forming organisms.
How can we reduce carbon dioxide emissions?
We can reduce co2 emissions by transitioning to renewable energy sources, protecting and restoring forests, and investing in carbon capture and storage technologies.