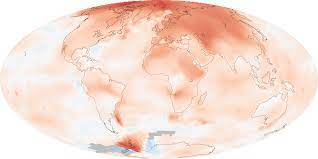
The Arctic, a remote and enigmatic region, has been experiencing rapid and unprecedented changes in recent years. This phenomenon, known as Arctic amplification, has garnered significant attention from scientists, environmentalists, and policymakers alike. In this article, we will delve deep into the heart of the Arctic, exploring what Arctic amplification is, its causes, consequences, and what it means for our planet’s climate system.
Understanding Arctic Amplification
To comprehend Arctic amplification, we must first grasp the basics of the Arctic climate system. The Arctic, characterized by its extreme cold and unique geography, plays a vital role in regulating global climate patterns. It acts as Earth’s air conditioner, helping to maintain temperature equilibrium.
The Role of Sea Ice
Sea ice in the Arctic Ocean is a critical component of this system. During the summer, it reflects sunlight, preventing excessive warming. In winter, it releases heat, preventing extreme cooling. However, over the past few decades, the Arctic has been losing its ice cover at an alarming rate.
Greenhouse Gas Effect
One of the primary drivers of Arctic amplification is the greenhouse effect. Human activities, such as the burning of fossil fuels, have released an abundance of greenhouse gases into the atmosphere. These gases trap heat, leading to an overall rise in global temperatures. The Arctic, being especially sensitive, experiences this warming at a much higher rate.
Causes of Arctic Amplification
Several factors contribute to Arctic amplification, and they all interact in complex ways. Understanding these causes is crucial for devising effective strategies to mitigate its impact.
Albedo Feedback
As the Arctic ice melts, it exposes darker ocean waters underneath. These darker surfaces absorb more sunlight, further accelerating the warming process—a feedback loop known as the albedo effect.
Changes in Atmospheric Circulation
Shifts in atmospheric circulation patterns can push warm air into the Arctic, exacerbating temperature increases. The polar vortex, a circulating air mass around the North Pole, has become more unstable in recent years, leading to more frequent and severe winter weather events in some regions.
Consequences of Arctic Amplification
The consequences of Arctic amplification are far-reaching and affect not only the polar region but the entire planet.
Rising Sea Levels
The melting of Arctic glaciers and ice sheets contributes significantly to rising sea levels. This poses a grave threat to coastal communities worldwide.
Disruption of Ecosystems
Arctic ecosystems, finely tuned to the extreme conditions, face disruption. Species like polar bears, seals, and walruses are struggling to adapt to rapidly changing habitats.
Impact on Weather Patterns
Arctic amplification can influence weather patterns across the globe. It has been linked to more frequent and severe weather events, such as hurricanes and droughts.
The Human Connection
It’s easy to think of the Arctic as a distant, frozen wasteland with little impact on our daily lives. However, Arctic amplification is a stark reminder that our actions have global consequences. The choices we make regarding fossil fuel consumption, greenhouse gas emissions, and environmental conservation directly affect the fate of the Arctic and, by extension, the entire planet.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Arctic amplification is a complex and pressing issue that demands our attention. Its causes and consequences are deeply intertwined with the health of our planet. To combat this phenomenon, we must take immediate and concerted actions to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, protect Arctic ecosystems, and raise awareness about the critical role the Arctic plays in our global climate system.
FAQs
What is Arctic amplification?
Arctic amplification refers to the phenomenon where the Arctic region is warming at a rate much faster than the global average, leading to various environmental changes.
Why should we be concerned about Arctic amplification?
We should be concerned because it has global implications, including rising sea levels, disruptions to ecosystems, and altered weather patterns.
What can individuals do to help mitigate Arctic amplification?
Individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by using energy-efficient appliances, driving less, and supporting policies and initiatives aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Are there any positive aspects to Arctic amplification?
While it may open up new shipping routes, the negative consequences, such as rising sea levels and ecosystem disruptions, far outweigh any potential benefits.
How can governments and international organizations address Arctic amplification?
Governments and international organizations must work together to enforce stricter environmental regulations, promote renewable energy sources, and support scientific research in the Arctic region to monitor and mitigate the effects of amplification.